
Heatwaves are prolonged periods of excessively hot weather, which may be accompanied by high humidity. Heatwaves are associated with high pressure (anti-cyclonic flow) in the middle atmosphere (about 3 to 7 km) which causes a downward motion of air [subsidence]. This downward motion causes the air below to get compressed and heat up.
Major causes of heatwaves:
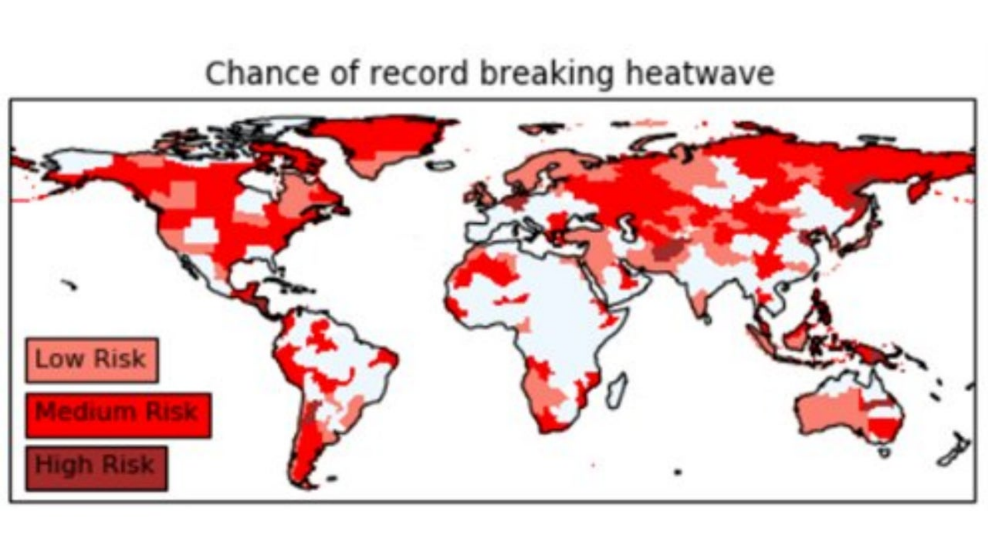
The frequency, duration, and intensity of heatwaves have been increasing globally due to climate change. El Niño also has an important role to play in the genesis of heatwaves over India
Rising Incidence of Heatwaves: The IPCC reports that every additional 0.5°C of global warming significantly raises the likelihood of extreme heat events. For instance, record-breaking temperatures were observed in July 2023, marking some of the hottest days ever recorded. In recent years, the heatwaves occurred in rapid succession in 2016, 2018, 2019, 2022, and 2023 in India .
Consequences of Heatwaves
Health Impacts: Heatwaves pose severe health risks, leading to heat-related illnesses and increased mortality rates, particularly among vulnerable populations such as the elderly and outdoor workers. The WHO estimates that approximately 489,000 heat-related deaths occur annually.
Agricultural Stress: High temperatures can severely affect crop yields and livestock productivity. Heat stress impairs plant growth and can lead to crop failures, threatening food security.
Environmental Degradation: Heatwaves contribute to soil desiccation and reduce water availability in rivers and groundwater reserves, impacting ecosystems and biodiversity. They also increase the risk of wildfires, as seen during the 2010 Russian heatwave that devastated millions of hectares of forest. Marine heatwaves can lead to coral bleaching and shifts in fish populations, disrupting local fisheries. Climate forecast says the Indian Ocean will very likely experience surface warming of 1.4-3°C between 2020 and 2100.
Economic Consequences: The economic impact of heatwaves is significant, affecting productivity across various sectors. Increased energy demands for cooling can strain power supplies, leading to outages.
Conclusion
The rising incidence of heatwaves is a critical issue linked to climate change that poses serious threats to human health, agricultural productivity, and environmental stability. Addressing this challenge requires urgent action to mitigate climate change through reduced greenhouse gas emissions and enhanced adaptation strategies to protect vulnerable populations and ecosystems.