
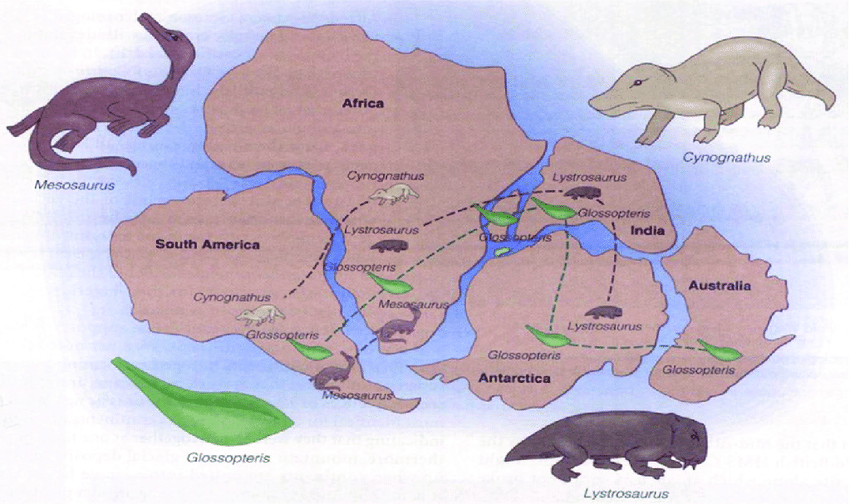
The distribution of plants and animals across the globe is influenced by a multitude of factors that can be broadly categorized into abiotic (non-living) and biotic (living) components, as well as human activities.
Abiotic Factors
Biotic Factors
Human Activities
Conclusion
These factors collectively determine the complex and dynamic patterns of plant and animal distribution across the globe.