

Q. 1: Which of the following is correctly matched?
Answer: B
Explanation:
Tughlaq Nama (Book of the Tughlaqs), was written in the year 1320 by Amir Khusrau. It is a historic masnavi (an extensive poem) of the reign of the Tughlaq dynasty that describes the tragedy of Deval Devi.
Chand Bardai was an Indian poet, who composed Prithviraj Raso, an epic poem in Brajbhasa about the life of the Chahamana king Prithviraj Chauhan. The poem presents him as a court poet of Prithviraj.
Kalhana was the author of Rajatarangini (River of Kings), an account of the history of Kashmir. He wrote the work in Sanskrit between 1148 and 1149.
Gita Govinda is written by Jayadeva. Gita Govinda is written in Sanskrit during the twelfth century and was performed in many venues including the Puri temple.
Q. 2: Consider the following statements:
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
Explanation:
The Group of 24 (G-24) is a chapter of the Group of 77 (G-77), the largest intergovernmental group of developing states in the United Nations (UN). The G-24’s full name is the Intergovernmental Group of Twenty-Four on International Monetary Affairs and Development.
The G-24 was established in 1971 to coordinate the positions of developing countries on international monetary and development finance issues. The G-24’s objectives include:
The G-24 meets twice a year, before the International Monetary and Financial Committee and Development Committee meetings of the IMF and World Bank. The G-24’s permanent secretariat is located in Washington, DC
The G7 is an informal bloc of industrialized democracies—the United States, Canada, France, Germany, Italy, Japan, and the United Kingdom (UK)—that meets annually to discuss issues such as global economic governance, international security, and, most recently, artificial intelligence (AI).
Q. 3: Consider the following statements:
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
Answer: A
Explanation:
The Brahmaputra River System is a major river basin in Central and South Asia that includes the Brahmaputra River and its many tributaries:
The Brahmaputra River is known as the Tsangpo river in Tibet.
Origin: The Brahmaputra originates in the Kailash ranges of the Himalayas in southern Tibet, China.
Course: The Brahmaputra flows through the Tibet Autonomous Region of China, the Indian states of Arunachal Pradesh and Assam, and Bangladesh. It eventually joins the Ganges River and empties into the Bay of Bengal.
Length: The Brahmaputra is about 2,900 kilometers long, making it one of the longest rivers in Asia. But in India, Brahmputra length is only 916 km. The length of the Ganga river is about 2525 km.
Tributaries: The Brahmaputra has many tributaries, including the Kyi, Chu, Dihang, Lohit, Subansiri, Burhi Dihing, Kopili, Jia Bhareli, Manas, Gangadhar, and Tista. The Subansiri is the largest tributary.
Q. 4: Consider the following statements:
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
Answer: B
Explanation:
Tebhaga Movement (1946-47): It was a peasant resistance that erupted in Bengal in 1946-47 under the leadership of Bangiya Pradeshik Kisan Sabha (BPKS). It demanded a reduction in the jotedars’ (landlords) share in the crop harvest from half to one-third.
The Tebhaga Movement was a significant peasant agitation that took place in Bengal from 1946 to 1947. It was initiated by the All India Kisan Sabha, the peasant front of the Communist Party of India. The term “Tebhaga” means “three shares,” reflecting the movement’s primary demand: sharecroppers (tenants) wanted two-thirds of the produce from the land, leaving one-third for the landlords.
The movement was marked by intense and sometimes violent protests, as sharecroppers sought to reduce the landlords’ share of the harvest. It occurred on the eve of India’s independence and the partition of Bengal, making it one of the most intense peasant revolutions in Indian history.
Q. 5 : Which of the following words were added in the Preamble by the 42nd Constitutional Amendment Act?
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
Answer: B
Explanation:
The 42nd Constitutional Amendment Act of 1976 added the words “Socialist” and “Integrity” to the Preamble of the Indian Constitution. The word “Fraternity” was already present in the original Preamble.
Q. 6: Consider the following statements:
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
Answer: B
Explanation:
The Model Code of Conduct is not a constitutional provision; it is a set of guidelines issued by the Election Commission of India to regulate political parties and candidates prior to elections.
Part XV of the Indian constitution deals with elections: This is correct. Part XV of the Indian Constitution deals with elections and includes provisions related to the Election Commission and the conduct of elections.
Q. 7: Consider the following statements:
Which of the above statements are correct?
Answer: A
Veto Power of the President of India is guided by Article 111 of the Indian Constitution. Article 111 deals with the President’s power to give assent to bills passed by the Parliament, including the power to withhold assent (veto).
Article 200 of the Indian Constitution deals with the powers of the Governor with regard to assent given to bills passed by the State legislature and other powers of the Governor such as reserving the bill for the President’s consideration.
Article 112 deals with the annual financial statement (budget) of the Government of India, not the powers of the Governor.
Q. 8 : Consider the following pairs:
Judicial Doctrines Important Judgements Associated
Which of the pairs given above is/are correctly matched?
Answer: A
Explanation:
Doctrine of Severability – A.K. Gopalan v. State of Madras (1950): This is correctly matched. The Doctrine of Severability was discussed in this case.
Doctrine of Basic Structure – Minerva Mills Ltd. v. Union of India (1980): This is correctly matched. The Doctrine of Basic Structure was reaffirmed in this case.
Doctrine of Pith and Substance – Indira Nehru Gandhi v. Raj Narain (1975): This is incorrectly matched. The Doctrine of Pith and Substance is not associated with this case.
The Doctrine of Pith and Substance is actually associated with the case State of Bombay v. F.N. Balsara (1951), not Indira Nehru Gandhi v. Raj Narain (1975). This case is significant for several reasons, including its application of the Doctrine of Basic Structure. The Doctrine of Pith and Substance is used to determine the true nature of legislation when there is a conflict between the powers of different legislative bodies.
Q. 9 : Which of the following are features of the Indian Parliamentary System are:
Choose from the following options;
Explanation:
Independent Judiciary: While important, this is not a feature specific to the parliamentary system.
Collective responsibility of the executive to the legislature: This is a key feature of the parliamentary system.
A written Constitution: This is not specific to the parliamentary system; many countries with different systems have written constitutions.
Presence of de jure and de facto executives: This is a feature of the parliamentary system, where the head of state (de jure) and the head of government (de facto) are separate.
Individual responsibility of the executive to the legislature: This is also a feature of the parliamentary system, where ministers are individually responsible to the legislature.
Q. 10 : Through which of the following acts the foundation of Central Administration was laid in India?
Answer: B
Explanation: The Regulating Act of 1773 laid the foundation of central administration in India. It was the first step taken by the British government to control and regulate the affairs of the East India Company, establishing a central administrative system in British India.
Q.11: Which of the following statements are true about the state governor?
Choose from the following options;
Answer: B
Explanation:
The Governor of a state in India has the executive power of the state: The Constitution of India also specifies the following eligibility requirements for a Governor:
The Governor of a State is appointed by the President for a term of five years and holds office during his pleasure. Only Indian citizens above 35 years of age are eligible for appointment to this office. Executive power of the State is vested in Governor.
A Governor holds office during the pleasure of the President of India. Article 156: The Governor’s term is generally five years, but the President can remove them at any time.
The Constitution does not specify the grounds for the removal of a Governor.
Q. 12 : With reference to India, consider the following statements:
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
Answer: B
Explanation:
Government law officers and legal firms are recognized as advocates, but corporate lawyers and patent attorneys are excluded from recognition as advocates: This is incorrect. Corporate lawyers and patent attorneys can also be recognized as advocates if they meet the criteria set by the Bar Council of India.
Bar Councils have the power to lay down the rules relating to legal education and recognition. the Bar Council of India (BCI) has the power to lay down rules for legal education and recognition of law colleges. The BCI sets standards for legal education in India, including the length of courses, the number of class hours, and the affiliation requirements for law colleges.
Q. 13 : Consider the following statements:
Which of the statements given above are correct?
Explanation:
A bill amending the Constitution requires a prior recommendation of the President of India: This is incorrect. A Constitution Amendment Bill does not require the prior recommendation of the President.
When a Constitution Amendment Bill is presented to the President of India, it is obligatory for the President of India to give his/her assent: This is incorrect. The President can neither withhold assent nor return the bill for reconsideration.
A Constitution Amendment Bill must be passed by both the Lok Sabha and Rajya Sabha by a special majority and there is no provision for joint sitting: This is correct. A Constitution Amendment Bill must be passed by both Houses of Parliament by a special majority, and there is no provision for a joint sitting in case of disagreement.
Q. 14: Consider the following statements:
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
Answer: B
Explanation:
The Constitution of India classifies the ministers into four ranks viz. Cabinet Minister, Minister of State with Independent Charge, Minister of State and Deputy Minister: This is incorrect. The Constitution does not classify ministers into these specific ranks; this classification is based on conventions and administrative practices.
The total number of ministers in the Union Government, including the Prime Minister, shall not exceed 15 percent of the total number of members in the Lok Sabha: This is correct. This provision is specified under the 91st Amendment Act of 2003.
Q. 15 : With reference to anti-defection law in India, consider the following statements:
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
Answer: B
Explanation:
The law specifies that a nominated legislator cannot join any political party within six months of being appointed to the House: This is incorrect. The law allows a nominated legislator to join a political party within six months of being appointed to the House.
The law does not provide any time-frame within which the presiding officer has to decide a defection case: This is correct. The anti-defection law does not specify a time-frame for the presiding officer to decide on a defection case.
Q.16: Consider the following statements regarding the National Emergency (Article 352):
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
Answer: A
Explanation:
President proclaims a national emergency only after receiving a written recommendation from the cabinet: This is correct. According to Article 352 of the Indian Constitution, the President can proclaim a national emergency only after receiving a written recommendation from the Union Cabinet.
President can declare a national emergency only on the actual occurrence of war or external aggression: This is incorrect. The President can declare a national emergency not only on the actual occurrence of war or external aggression but also in the case of imminent danger of such events, as well as in the case of armed rebellion.
Q. 17 : Members of Election Commission are appointed by……..
Answer: A
Explanation: Members of the Election Commission of India, including the Chief Election Commissioner and other Election Commissioners, are appointed by the President of India.
Q. 18 : Which one of the following Articles describes the Independent Judiciary?
Answer: B
Explanation: Article 124 of the Indian Constitution deals with the establishment and constitution of the Supreme Court of India, which is the apex court and ensures the independence of the judiciary.
Q. 19: Which of the following can be considered as discretionary powers of the Governor?
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
Answer: C
Explanation:
Reservation of a bill for the consideration of the President: This is a discretionary power of the Governor.
Pardoning powers of the Governor: This is not a discretionary power; it is exercised on the advice of the Council of Ministers.
Recommendation for the imposition of the President’s Rule in the state: This is a discretionary power of the Governor.
Dissolution of the state legislative assembly if the council of ministers loses majority: This is a discretionary power of the Governor.
Q. 20 : Which one of the following Fundamental Rights incorporates the Right to Elementary Education?
Answer: A
Explanation: The Right to Elementary Education is incorporated under Article 21A of the Indian Constitution, which falls under the Cultural and Educational Rights. This article mandates free and compulsory education for all children aged 6 to 14 years.
Q. 21 : Consider the following statements with reference to Forward Policy of the British colonial power in India:
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
Answer: A
Explanation:
It was propounded by Auckland: This is correct. The Forward Policy was advocated by Lord Auckland, who was the Governor-General of India from 1836 to 1842.
It led to the conflict between the British and Sikh Empire under Ranjit Singh: This is incorrect. The Forward Policy primarily aimed at countering Russian influence in Central Asia and Afghanistan, and it did not directly lead to a conflict with the Sikh Empire under Ranjit Singh.
Q. 22 : Which of the following was the primary objective of the Fraser Commission of 1903?
Answer: A
Explanation: The Fraser Commission of 1903 was established to investigate the working of the police administration in British India and to suggest improvements for its efficiency.
Q. 23 : With reference to the Ryotwari settlement, consider the following statements:
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
Answer: C
Explanation:
The Ryotwari Settlement system was introduced in British India by Thomas Munro and Alexander Reed: This is correct. Thomas Munro and Captain Alexander Read introduced the Ryotwari system in the late 18th century, and it was formalized by Munro in 1820.
Under this system, the British government collected land revenue directly from the ryots: This is correct. The Ryotwari system established a direct relationship between the British government and the cultivators (ryots), bypassing intermediaries.
Q. 24 : Consider the following statements regarding the Treaty of Amritsar (1809):
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
Answer: B
Explanation:
It was signed between Maharaja Ranjit Singh and the Governor General Lord Hastings: This is incorrect. The Treaty of Amritsar (1809) was signed between Maharaja Ranjit Singh and Charles T. Metcalfe, representing the British East India Company.
It recognized Maharaja Ranjit Singh’s sovereignty over the Sikh Empire while defining its boundaries with British territories: This is correct. The treaty recognized Ranjit Singh’s sovereignty over the Sikh Empire and defined the Sutlej River as the boundary between his territories and those of the British.
Q. 25 : The ‘Project NAMAN,’ sometimes seen in the news, is associated with:
Answer: B
Explanation: Project NAMAN is an initiative by the Indian Army designed to provide dedicated support and services to Defence Pensioners, Veterans, and their families. It involves the establishment of Common Service Centres (CSCs) across India, enabled by the SPARSH (System for Pension Administration Raksha) digital pension system.
Q. 26 : Which of the following statements best describes the SEHER Program, recently seen in the news?
Answer: C
Explanation:
The SEHER Program, launched by the Women Entrepreneurship Platform (WEP) and TransUnion CIBIL, aims to empower women entrepreneurs in India by providing them with financial literacy content and business skills. This initiative helps women entrepreneurs access and manage credit, thereby contributing to their business growth and economic development.
Q. 27 : Consider the following statements with respect to ‘Naxalbari uprising’
Select the correct statements
Answer: B
Explanation:
Naxalbari uprising: It was an armed peasant revolt in 1967 in the Naxalbari block of Siliguri subdivision in Darjeeling district, West Bengal, India. It was mainly led by local tribals and the radical communist leaders of Bengal and further developed into Communist Party of India (Marxist–Leninist) in 1969.
The uprising occurred in such a situation that a great turmoil was going on with in the communist organisations of the world and also the Indian nation following the Sino-Soviet split.
The leader and ideologue of the uprising Charu Majumdar presumed that the time was ripe for launching an armed protracted people’s war in India following the Chinese Revolution (1949), Vietnam War and Cuban Revolution.
It was mainly led by local tribals and the radical communist leaders of Bengal and further developed into Communist Party of India (Marxist–Leninist) in 1969.
It was initiated in Bengal by the Kisan Sabha: This is incorrect. The Naxalbari uprising was initiated by radical communist leaders and tribals in the Naxalbari region of West Bengal.
The movement resulted in clashes between Jotedars and Bargadars: This is correct. The movement led to violent clashes between the Jotedars (landlords) and Bargadars (sharecroppers)
Q. 28 : ‘Sangam Literature’ was patronised by ______________ .
Answer: A
Explanation: Sangam literature was patronized by the Pandya, Chera, and Chola dynasties. These Tamil dynasties supported the literary assemblies known as Sangams, where poets and scholars gathered to create and preserve Tamil literature
Q. 29 : Which place of Odisha is called as Dandi?
Answer: C
Explanation: Inchudi in Odisha is often referred to as the “Second Dandi” because it was a significant site during the Salt Satyagraha led by Mahatma Gandhi. The salt march in Odisha began from Inchudi and played a crucial role in the Indian independence movement
Q. 30 : Which of the following leads to termination of Session of a House?
Answer: C
Explanation:
An adjournment suspends the work in a sitting for a specified time, which may be hours, days or weeks. In this case, the time of reassembly is specified. An adjournment only terminates a sitting and not a session of the House. The power of adjournment lies with the presiding officer of the House.
Adjournment sine die means terminating a sitting of Parliament for an indefinite period. In other words, when the House is adjourned without naming a day for reassembly, it is called adjournment sine die. The power of adjournment sine die lies with the presiding officer of the House.
Prorogation means the termination of a session of the House by an order made by the President under article 85(2)(a) of the Constitution. Prorogation terminates both the sitting and session of the House. Usually, within a few days after the House is adjourned sine die by the presiding officer, the President issues a notification for the prorogation of the session. However, the President can also prorogue the House while in session.
A dissolution ends the very life of the existing House, and a new House is constituted after general elections are held. Rajya Sabha, being a permanent House, is not subject to dissolution. Only the Lok Sabha is subject to dissolution.
Q. 31 : Consider the following statements;
Select the correct statement
Answer: A
Explanation:
A hot spring, hydrothermal spring, or geothermal spring is a spring produced by the emergence of geothermally heated groundwater onto the surface of the Earth.
Geysers are hot springs that intermittently spout a column of hot water and steam into the air. This action is caused by the water in deep conduits beneath a geyser approaching or reaching the boiling point.
Hot springs are heated by geothermal heat—heat from the Earth’s interior. In volcanic areas, water may come into contact with very hot rock heated by magma. A Hot Spring, also known as a geothermal spring is a naturally occurring spring of water that emerges due to heated groundwater. The heat produced is either through the magma within the Earth’s crust or through the movement of fault in the crust.
Panamik, Nubra Valley ,Chumathang (Ladakh) Taptapani (Odisha) and Atri (Odisha) are few examples
Q. 32 : Consider the following statements:
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
Answer: A
Explanation:
Net Area Sown: The physical extent of land on which crops are sown and harvested is known as net sown area. This represents the total area sown with crops and orchards. Area sown more than once in the same year is counted only once.
Gross Cropped Area: This represents the total area sown once and/or more than once in a particular year, i.e. the area is counted as many times as there are sowings in a year. This total area is also known as total cropped area or total area sown.
Current Fallow Land: The cultural practice adopted to give rest to the land is known as fallowing. The land recoups the lost fertility through natural processes. Under current fallow land, the land is left without cultivation for less than one or one agricultural year.
Fallow other than Current Fallow: When the cultivable land is left uncultivated for more than a year but less than five years, it is categorized as fallow other than current fallow.
Culturable Wasteland : If the land is left uncultivated for more than five years, it would be categorized as culturable wasteland
Q. 33 : Where can we find maximum number of earthquakes in the earth surface?
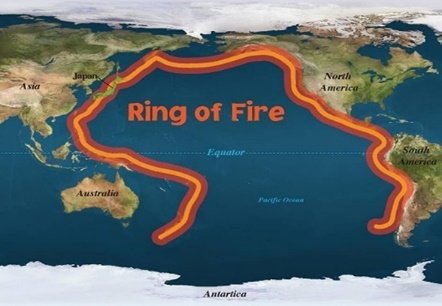 Answer: A
Answer: A
Explanation:
The world’s greatest earthquake belt, the circum-Pacific seismic belt, is foundalong the rim of the Pacific Ocean, where about 81 percent of our planet’s largestearthquakes occur. It has earned the nickname “Ring of Fire”.
Q. 34 : Suitable sea-surface temperatures for tropical cyclone formation:
Answer: C
Explanation:
Tropical Cyclone suitable conditions:
The six basic suitable conditions for tropical cyclone formation are:
1. Sea-surface temperatures of at least 26.5 degrees Celsius or 80 degrees Fahrenheit (usually). A deep warm layer of water beneath the ocean surface (of at least 50 meters or so) can be helpful, but is not necessarily required.
2. A location (usually) at least five degrees of latitude (roughly 300 nautical miles) away from the equator.
3. A pre-existing disturbance (cluster of showers and thunderstorms) with favorable low-level spin and convergence in the lower half of the troposphere.
4. Low values of vertical wind shear between roughly 5,000 and 38,000 feet (generally less than 10 meters per second, or 20 knots).
5. A middle troposphere (roughly from about 10,000 to 20,000 feet) that is relatively moist (has moderate to high relative humidity).
6. A troposphere that is neutrally stable or unstable with respect to rising moist air parcels (environmental lapse rates must not be too stable such that thunderstorm development is greatly inhibited).
Q. 35: Which waves caused by the earthquakes cause maximum damage and destruction on earth’s surface?
Answer: B
Explanation:
Types of Seismic Waves
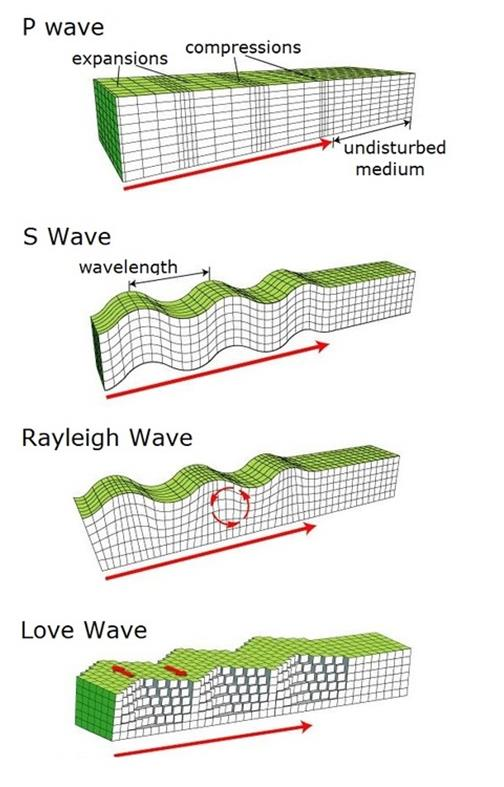 There are several differentkinds of seismic waves, and they allmove in different ways. The two maintypes of waves are body waves andsurface waves. Body waves can travelthrough the earth’s inner layers, butsurface waves can only move along thesurface of the planet like ripples on water. Earthquakes radiate seismic energy as both body and surface waves.
There are several differentkinds of seismic waves, and they allmove in different ways. The two maintypes of waves are body waves andsurface waves. Body waves can travelthrough the earth’s inner layers, butsurface waves can only move along thesurface of the planet like ripples on water. Earthquakes radiate seismic energy as both body and surface waves.
BODY WAVES: Traveling through the interior of the earth, body waves arrive before the surface waves emitted by an earthquake. These waves are of a higher frequency than surface waves. P and S waves are examples of body waves.
SURFACE WAVES: Travelling only through the crust, surface waves are of a lower frequency than body waves, and are easily distinguished on a seismogram as a result. Though they arrive after body waves, it is surface waves that are almost entirely responsible for the damage and destruction associated with earthquakes. This damage and the strength of the surface waves are reduced in deeper earthquakes. Love and Rayleigh wave are examples of surface waves.
During an earthquake, surface waves cause the most damage. Unlike other seismic waves that move deep inside the Earth, surface waves move along just under the surface of the Earth like waves in water. Surface waves are the slowest seismic waves and are the final waves to hit an area after an earthquake.
Rayleigh waves cause both vertical and horizontal ground motion. These can be the mostdestructive waves as they roll along lifting and dropping the ground as they pass.
Q. 36 : Which one of the following rocks is transformed into marble?
Answer: c
Explanation:
Q. 37 : Consider the following statements :
Assertion (A) : The mineral wealth of India is largely confined to the peninsular India.
Reason (R ) : Peninsular India has enormous quantity of Igneous & Metamorphic rocks.
Now select your answer according to the coding scheme given below :
Answer: B
Explanation:
Assertion (A): The mineral wealth of India is largely confined to the peninsular India. This is correct. The peninsular region of India is rich in minerals.
Reason (R): Peninsular India has an enormous quantity of igneous and metamorphic rocks. This is also correct and is one of the reasons for the mineral wealth in the region
Q. 38 : Indravati is a tributary of
Answer: B
Explanation:
Q. 39 : Choose the correct pair;
Boundary line : between India and neighbour country
Choose the correct pair(s)
Answer: D
Explanation:
McMahon Line – India and China: This is correct. The McMahon Line is the boundary between India and China.
Radoliff Line – India and Nepal: This is correct. The Radcliffe Line is the boundary between India and Nepal: .
Radcliffe Line – India and Pakistan: This is correct. The Radcliffe Line is the boundary between India and Pakistan.
Q. 40: Sunda Strait, that was making up news recently, separates which two islands?
Answer: A
Explanation: Explanation: The Sunda Strait is a narrow body of water that separates the Indonesian islands of Java and Sumatra
Q. 41: If the earth had no satellite of its own i.e., the moon, which of the following phenomena will not occur ?
Answer: C
Explanation:
If the earth had no satellite of its own i.e., the moon, then Spring tides will not happen.
The moon has a significant impact on tides, due to the gravitational attraction of the moon on the Earth’s water. This effect is magnified when the moon’s gravitational attraction aligns with the gravitational pull of the sun. This produces the highest high tides and lowest low tides, known as spring tides. When the pull of the moon and the sun are perpendicular to each other, the lowest high tides and highest low tides, collectively termed neap tides, are produced. While ocean currents are primarily affected by winds and the Coriolis force, tides can have a large impact on currents near the coasts.
Q. 42: Consider the following statements :
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
Answer: C
Explanation:
The aurora borealis is a display of natural light in the sky near the North Pole. Itwas named after the Roman goddess of the dawn, Aurora, and the Greek name for thenorth wind, Boreas, by Pierre Gassendi in 1621. It is a result of photon emissions in theearth’s upper atmosphere from ionized nitrogen atoms regaining an electron, and oxygenand nitrogen atoms returning from an excited state to a low-energy state.
Q. 43: One of the blood vessel carries oxygenated blood directly to the heart muscle. Identify it
Answer: A
Explanation:
The aorta (the main blood supplier to the body) branches off into two main coronary blood vessels (also called arteries). These coronary arteries branch off into smaller arteries, which supply oxygen-rich blood to the entire heart muscle. The right coronary artery supplies blood mainly to the right side of the heart.
The deoxygenated blood is carried to the lungs for oxygenation through the pulmonary artery. It is then pumped to the heart via the pulmonary vein for circulation to various tissues.
Q. 44: Consider the following statements :
Which of the above statements are correct ?
Answer: D
Explanation:
The President of India appoints the leader of the majority party in Lok Sabha as Prime Minister. Prime Minister is also the chief adviser to the President of India and head of the Council of Ministers. Prime Minister is the senior member of cabinet in the executive branch of government in a parliamentary system.
The Prime Minister is responsible for aiding and advising the President in the distribution of work of the Government to various ministries and offices and in terms of the Government of India (Allocation of Business) Rules, 1961. The co-ordinating work is generally allocated to the Cabinet Secretariat. While generally the work of the Government is divided into various Ministries, the Prime Minister may retain certain portfolios if they are not allocated to any member of the cabinet.
The person who is not a member of either house of Parliament can be appointed as Prime Minister. But within six months he should become the member of either house of Parliament otherwise he ceases to be the Prime Minister. This was held in Supreme Court in 1997.
Q. 45: Consider the following statements :
Which of the above statements are correct ?
Answer: C
Explanation:
A Bill may be introduced in either House of Parliament. However, a Money Bill can not be introduced in Rajya Sabha. It can only be introduced in Lok Sabha with prior recommendation of the President for introduction in Lok Sabha. If any question arises whether a Bill is a Money Bill or not, the decision of the Speaker thereon is final.
The Finance Bill can be introduced only in Lok Sabha. However, the Rajya Sabha can recommend amendments in the Bill. The bill has to be passed by the Parliament within 75 days of its introduction.
Rajya Sabha is required to return a Money Bill passed and transmitted by Lok Sabha within a period of 14 days from the date of its receipt. Rajya Sabha may return a Money Bill transmitted to it with or without recommendations. It is open to Lok Sabha to accept or reject all or any of the recommendations of Rajya Sabha.
However, if Rajya Sabha does not return a Money Bill within the prescribed period of 14 days, the Bill is deemed to havebeen passed by both Houses of Parliament at the expiry of the said period of 14 days in the form in which it was passed by Lok Sabha.
Like Money Bills, Bills which, inter alia, contain provisions for any of the matters attracting sub-clauses (a) to (f) of clause (1) of article 110 can also not be introduced in Rajya Sabha. They can be introduced only in Lok Sabha on the recommendation of the President. However, other restrictions in regard to Money Bills do not apply to such Bills.
Q. 46: Consider the following statements :
Which of the above statements are correct ?
Answer: A
Explanation:
The judges of a high court are appointed by the President. The chief justice is appointed by the President after consultation with the chief justice of India and the governor of the state concerned.
A notice must be given at least 14 days before form the date of moved motion. And such resolution must be passed by the two-third of total membership of both the House. So it is quite clear that Judges of Supreme Court and High Court cannot be Impeached only the President of Indian can Impeached.
A judge of the supreme court or High court is removed by the Process of impeachment. The President is authorised to remove the judge from his office only after an address by the Parliament has been presented to him in the same session for such removal. The address must be supported by a special majority of each house of the Parliament. (Majority of the total membership of that House and a majority of not less than two-thirds of the member of that House present and voting).
The sitting judges of High Court are entitled to salaries, allowances and privileges as parliament from time to time determine. The expense of salaries and allowances of the High court judges are charged upon the Consolidated Fund of the State.
Q. 47: Consider the following :
LIST – I LIST – II
Which is the correct match ?
Answer: C
Explanation:
A Sonar is a device that uses sound waves to detect objects. In the fishing industry, a Sonar is used to detect fish, structure, and the seafloor around the vessel, while a fish finder detects these objects directly under the vessel.
A radar speed gun (also radar gun and speed trap gun) is a device used to measure the speed of moving objects.
A laser is a device that emits light through a process of optical amplification based on the stimulated emission of electromagnetic radiation. The word “laser” is an acronym for “light amplification by stimulated emission of radiation”. It helps in identifying and quantitatively determining the presence of specific gaseous constituents.
Fluid filled small bowel loops on CT scan is a very common and frequently normal finding. By itself, this means nothing that is significant. Even in the setting of abdominal pain or other symptoms, this finding by itself is not clinically significant.
Q. 48: Minimum Alternate Tax (MAT), often in news is
Answer: A
Explanation: Minimum Alternate Tax (MAT) is a provision in India’s Income Tax Act that ensures companies with substantial book profits pay a minimum amount of income tax. It is applicable to all companies, including foreign companies, and is calculated based on the book profits of the company
Q. 49: Who among the following are eligible under portfolio investment scheme (PIS)?
Select the correct answer code:
Answer: D
Explanation:
Foreign Institutional Investors (FIIs), Non-Resident Indians (NRIs), and Persons ofIndian Origin (PIOs) are allowed to invest in the primary and secondary capital markets inIndia through the portfolio investment scheme (PIS). Under this scheme, FIIs/NRIs canacquire shares/debentures of Indian companies through the stock exchanges in India.
Q. 50: Which of the following policy measures may be used by the Government to reduce the Current Account Deficit (CAD)?
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
Answer: C
Explanation:
Increasing import duties: This measure can help reduce the Current Account Deficit (CAD) by making imported goods more expensive, thereby reducing the demand for imports.
Providing export subsidies: This measure can boost exports by making them more competitive in the international market, which can help reduce the CAD.
Q. 51: With reference to Incremental Capital Output Ratio (ICOR), consider the following statements.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
Answer: A
Explanation:
It is the ratio of annual investment to the annual increase in GDP: This is correct. The Incremental Capital Output Ratio (ICOR) measures the amount of capital investment needed to generate one unit of additional output (GDP).
High ICOR implies a more efficient economy: This is incorrect. A high ICOR indicates that more investment is needed to produce additional output, which implies lower efficiency. A lower ICOR is indicative of a more efficient economy.
Q. 52: Consider the following statements with reference to Cost Push inflation:
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
Answer: A
Explanation:
Cost-push inflation is determined by supply-side factors such as higher wages etc.: This is correct. Cost-push inflation occurs when the overall price levels rise due to increases in the cost of wages and raw materials.
Cost-push inflation can only occur when demand is relatively inelastic: This is incorrect. Cost-push inflation can occur regardless of the elasticity of demand. It is driven by supply-side factors, not by the demand side.
Q. 53: Which of the following is/are the instruments available with IMF to monetarily assist the member countries?
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
Answer: C
Explanation:
Reserve Tranche Position: This is an instrument available with the IMF to assist member countries. It represents the portion of a member country’s quota that can be accessed without conditions.
Contingent Reserve Arrangement: This is not an instrument of the IMF. It is associated with the BRICS countries.
Project Preparation Special Fund: This is not an instrument of the IMF. It is related to the Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank (AIIB).
Q. 54: Which of the following activities can be performed by the Small Financial Banks?
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
Answer: D
Explanation:
Small Finance Banks (SFBs) in India are governed by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI). The RBI regulates and supervises these banks to ensure they operate within the framework of the guidelines and policies set by the central bank. Small Finance Banks (SFBs) in India are permitted to perform the following activities:
Supplying credits to small and marginal farmers: SFBs are designed to provide financial services to underserved sections, including small and marginal farmers.
Supplying credits to micro and small industries: SFBs also cater to the credit needs of micro and small industries.
Being a business correspondent (BC) for another bank: SFBs can act as business correspondents for other banks, facilitating financial inclusion.
Q. 55: Consider the following differences between core and headline inflation:
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
Answer: B
Explanation:
Core Inflation reflects the rate of change in prices of all goods and services in an economy, whereas headline inflation excludes items that face volatile price movement: This is incorrect. Core inflation excludes items that face volatile price movements, such as food and energy prices, while headline inflation includes all items.
Generally, core inflation is the preferred tool for Central Banks to frame long-term policy: This is correct. Core inflation is often used by central banks to frame long-term monetary policy because it provides a clearer view of underlying inflation trends by excluding volatile items.
Q. 56: Consider the following statements regarding GVA (Gross Value Added) and GDP (Gross Domestic Product):
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
Answer: B
Explanation:
While GVA depicts the state of economic activity from the producers’ side, GDP depicts the demand perspective: This is incorrect. Both GVA and GDP can be used to measure economic activity from the production side. GVA measures the value added by producers, while GDP includes GVA plus taxes on products minus subsidies on products.
GVA is a better reflection of productivity than GDP as it excludes indirect taxes: This is correct. GVA is considered a better reflection of productivity because it excludes indirect taxes, which can distort the true value added by producers.
Q. 57: Which of the following represents National Income?
Answer: A
Explanation: National Income is typically measured as the Net National Product (NNP) at factor cost. It represents the total value of goods and services produced by a country’s residents, minus depreciation, and adjusted for the cost of production.
Q. 58: Consider the following statements:
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
Answer: A
Explanation:
Higher interest rate leads to lesser demand of money: This is correct. Higher interest rates generally reduce the demand for money because borrowing costs increase, making loans more expensive and saving more attractive.
Interest rate is decided by the Central Government: This is incorrect. In India, the interest rates are primarily decided by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI), not the Central Government.
Q. 59: Consider the following pairs:
Term: Meaning
Which of the pairs given above is/are correctly matched?
Answer: D
Explanation:
Q. 60: Which of the tools given below are used by RBI to control liquidity and inflation?
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
Answer: B
Explanation:
Increasing the tax base is not a tool used by the RBI; it is a fiscal policy measure typically managed by the government.
Q. 61: Consider the following statement related to Trade-Related Aspects of Intellectual Property Rights (TRIPS):
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
Answer: B
Explanation:
It completely prohibits compulsory licensing and government use of a patent without the authorization of its owner: This is incorrect. TRIPS does allow for compulsory licensing and government use of a patent without the authorization of its owner under certain conditions, such as in cases of national emergency or other circumstances of extreme urgency.
It allows members to exclude some types of plant and animal inventions from patenting in their countries: This is correct. TRIPS permits member countries to exclude certain types of plant and animal inventions from patentability.
Q. 62: Consider the following statements with respect to the trends in items under ‘Invisibles’ head of the Balance of Payment:
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
Answer: B
Explanation:
Transfers have constantly decreased in the last five years: This is incorrect. Transfers, particularly private transfers such as remittances, have shown an increasing trend over the past few years.
Services have constantly increased in the last five years: This is correct. The services sector, especially exports of software and IT services, has shown a steady increase.
Q. 63: Consider the following statements regarding the Special Economic Zone (SEZ):
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
Answer: B
Explanation:
It is set up under the provisions of Foreign Trade Policy: This is incorrect. Special Economic Zones (SEZs) in India are established under the Special Economic Zones Act, 2005, not the Foreign Trade Policy.
Both central and state governments have the power to establish SEZ: This is correct. Both the central and state governments have the authority to establish SEZs in India.
Q. 64: Consider the following statements regarding Micro and Small Enterprises (MSEs):
Which of the statements given above is/are not correct?
Answer: C
Explanation:
An enterprise is defined as a microenterprise where the investment in plant and machinery does not exceed ten crore: This is incorrect. A microenterprise is defined as one where the investment in plant and machinery does not exceed one crore rupees.
It is mandatory for every Central Ministry and PSUs to make at least 50% procurement from the MSE Sector: This is incorrect. The mandatory procurement target from the MSE sector is 25%, not 50%.
Q. 65: When a country faces the Balance of Payment crisis it takes the mechanism of,’ The Extended fund Facility (EFF)’ to recover the crisis. This service is provided by
Answer: B
Explanation:
The Extended Fund Facility (EFF) is a lending facility provided by the International Monetary Fund (IMF) to assist countries facing serious medium-term balance of payments problems due to structural weaknesses.
Q. 66: Which of the following statement regarding ‘import substitution’ is not correct?
Answer: D
Explanation: Import substitution is typically used by developing nations to reduce dependency on foreign goods by promoting domestic production. It involves protectionist measures like high tariffs and quotas to shield local industries from international competition.
Q. 67: Which among the following is/ are present only in plant cells?
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
Answer: B
Explanation:
Plastids are present only in plant cells. They are involved in photosynthesis (chloroplasts) and storage of starch (amyloplasts).
Vacuoles are present in both plant and animal cells, although they are much larger and more prominent in plant cells.
Mitochondria are present in both plant and animal cells, as they are essential for cellular respiration and energy production.
Q. 68: Which of the following is correct with regard to Bose-Einstein condensate?
Answer: A
Explanation: Bose-Einstein condensate (BEC) is a state of matter formed at temperatures close to absolute zero, where a group of atoms is cooled to near absolute zero. Under such conditions, a large fraction of the atoms occupy the lowest quantum state, causing quantum effects to become apparent on a macroscopic scale.
Q. 69: In the context of Indian economy, which of the following five-year plans proposed to achieve the two main objectives of ‘removal of poverty’ (Garibi Hatao) and ‘attainment of self-reliance’?
Answer: D
Explanation: The Fifth Five-Year Plan (1974-1978) aimed to achieve the two main objectives of ‘removal of poverty’ (Garibi Hatao) and ‘attainment of self-reliance’
Q. 70: Which of the following committees made recommendations with respect to Centre-State relations?
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
Answer: D
Explanation:
Sarkaria Commission: This commission was established in 1983 to examine and review the working of the existing arrangements between the Union and the States and to recommend changes.
M M Punchhi Commission: This commission was set up in 2007 to look into the new issues of Centre-State relations, keeping in view the changes that have taken place in the polity and economy.
Rajamannar Committee: This committee was set up by the Tamil Nadu government in 1969 to study Centre-State relations and recommend measures to improve them.
Q. 71: Consider the following statements:
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
Answer: C
Explanation:
Genetically Modified (GM) Crops:
GM crops are derived from plants whose genes are artificially modified, usually by inserting genetic material from another organism, in order to give it new properties, such as increased yield, tolerance to a herbicide, resistance to disease or drought, or improved nutritional value.
Earlier, India approved the commercial cultivation of only one GM crop, Bt cotton, but Genetic Engineering Appraisal Committee (GEAC) has recommended GM Mustard for commercial use.
Dhara Mustard Hybrid-11 (DMH-11) is an indigenously developed transgenic mustard. It is a genetically modified variant of Herbicide Tolerant (HT) mustard.
DMH-11 is a result of a cross between Indian mustard variety ‘Varuna’ and East European ‘Early Heera-2’ mustard.
Bt cotton: The only GM crop approved for commercial cultivation in India. Bt cotton was introduced in 2002 to combat bollworm infestation and has significantly improved cotton production, exports, and the textile industry.
GM mustard: The GEAC approved the environmental release of Mustard hybrid DMH-11 in 2022 for seed production and testing. However, the Supreme Court is hearing petitions filed by activists and an NGO on whether to allow transgenic food crops in farmer fields.
GM brinjal: The GEAC approved GM brinjal in 2009, but the United Progressive Alliance government put it on an indefinite moratorium due to public outrage. The GEAC has approved field trials of new varieties of indigenously developed Bt-brinjal in eight states from 2020 to 2023.
Other GM crops: India has granted biosafety authorizations for environmental release of genetically modified eggplant and mustard. India has also approved the importation of soybean and canola oils from select GM events.
New GM crops are approved on a case-by-case basis after a thorough scientific evaluation of their health and environmental safety.
Q. 72: Consider the following statements:
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
Answer: B
Explanation:
Genetic Engineering Appraisal Committee (GEAC): The Genetic Engineering Appraisal Committee (GEAC) is the technical body that evaluates proposals for genetically modified (GM) crop testing in India. The GEAC is under the Union Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEF&CC).
It is responsible for appraisal of activities involving large scale use of hazardous microorganisms and recombinants in research and industrial production from the environmental angle.
Q. 73: Consider the following statements:
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
Answer: C
Explanation:
Genome sequencing is a process of determining the complete DNA sequence of an organism’s genome. A genome is a complete set of DNA that contains all of the genes of an organism.
It involves figuring out the order of bases (Adenine, Cytosine, Guanines, and Thymine) that make up an organism’s DNA. It is supported by automated DNA sequencing methods and computer software to assemble the massive sequence data.
Gene: A gene is a specific segment of DNA that codes for the production of RNA and protein molecules. Genes are the fundamental units of heredity.
Q. 74: Consider the following statements:
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
Answer: C
Explanation:
|
Characteristics |
Gene Sequencing |
Gene Editing |
|
Definition |
The process of determining the precise order of nucleotides (A, T, C, G) in a DNA or RNA molecule. |
The process of making targeted modifications to the DNA sequence of a gene or genes. |
|
Purpose |
To obtain the complete or partial sequence of a gene, a set of genes, or an entire genome. |
To introduce desired changes, such as correcting genetic defects, modifying gene expression, or introducing new genetic traits. |
|
Techniques |
Sanger sequencing, Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS), and others. |
CRISPR-Cas9, zinc finger nucleases, TALENs, and other specialised tools. |
|
Outcome |
Provides information about the genetic makeup and composition of an organism. |
Allows for the direct manipulation and alteration of the genetic code. |
|
Modification |
Does not directly modify the genetic material. |
Enables the addition, removal, or alteration of specific DNA sequences. |
Q. 75: Consider the following statements:
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
Explanation:
DNA and RNA are both nucleic acids that carry genetic information, but they have several differences in structure and function:
Structure: DNA is double-stranded, while RNA is usually single-stranded. DNA is shaped like a ladder with two side rails and rungs that twist into a double helix. RNA is like a ladder that has been cut in half.
Sugar: DNA contains deoxyribose sugar, while RNA contains ribose sugar.
Bases: DNA contains the bases adenine, guanine, cytosine, and thymine. RNA contains the bases adenine, guanine, cytosine, and uracil, replacing thymine with uracil.
Q. 76: Consider the following statements:
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
Answer: D
Explanation:
Dispersion of light is the process by which white light separates into its individual colors: White light is made up of all colors in the visible spectrum, and each color has a unique index of refraction in materials other than a vacuum. When white light passes through a refracting medium, like a prism, the different colors bend at different angles because they have different wavelengths. This causes the light to spread out into its spectrum of colors, which appears as a rainbow.
Example: When white light passes through a prism, it splits into the colors of the rainbow, in order from violet to red.
Natural phenomenon: Rainbows are a natural example of dispersion of light. When sunlight passes through raindrops, the raindrops act as prisms and split the white light into its colors, forming a rainbow.
The refraction of light is the bending of light rays as they pass from one medium to another, thereby changing the path of the rays. Refraction occurs due to a change in the speed of the light ray or wave.
Total internal reflection, in physics, complete reflection of a ray of light within a medium such as water or glass from the surrounding surfaces back into the medium. The phenomenon occurs if the angle of incidence is greater than a certain limiting angle, called the critical angle.
Q. 77: Consider the following statements:
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
Answer: C
Explanation:
Probiotics and prebiotics are both foods and supplements that can help with gut health, but they work in different ways:
Probiotics: Live microorganisms, like bacteria or yeast, that are intended to improve the balance of good bacteria in the body. Probiotics can help with diarrhea, constipation, stomach pain, and overall gut health. They can be found in fermented foods like yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, pickles, miso, tempeh, kimchi, sourdough bread, and some cheeses.
Prebiotics: Non-digestible plant fibers that act as food for the good bacteria in the gut. Prebiotics can be found in foods like garlic, onions, bananas, whole grains, mushrooms, artichokes, asparagus, cabbage, chickpeas, oats, and wheat bread. Prebiotics are fermented in the colon into short-chain fatty acids, which can provide energy for the cells lining the gut wall.
Prebiotics and probiotics can support a healthy gut microbiome in different ways. Prebiotics feed the existing good bacteria, while probiotics add more good bacteria to the gut.
Q. 78: Consider the following statements:
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
Explanation:
Bisphenols are a group of organic compounds used in the manufacturing of many plastics and resins. They are commonly used to harden plastics and are found in a variety of consumer products, including: Food and beverage containers, Water pipes, Electronic equipment, Toys, and Dental sealants.
Some examples of bisphenols include:
Bisphenols can be harmful to the human body and environment:
Endocrine disruption: Bisphenols can disrupt the body’s endocrine system, which can lead to reproductive issues, mental health problems, and other health issues.
Environmental pollution: Bisphenols can contaminate the environment through plastic waste, which can take centuries to break down.
Q. 79: Consider the following statements:
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
Answer: C
Explanation:
Albert Einstein’s general theory of relativity is a physics theory that explains how gravity works and its relationship to other forces in nature:
Gravity is a result of the curvature of space and time, which can be stretched, warped, and pushed by matter. Gravity is strongest where space and time are most curved, and it vanishes where they are flat.
General relativity has predicted many phenomena that were observed years later, including black holes, gravitational waves, gravitational lensing, and the expansion of the universe.
General relativity is used to describe large-scale physical phenomena, such as planetary dynamics, the birth and death of stars, and the evolution of the universe.
Q. 80 : Consider the following statements about Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) :
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
Answer: B
Explanation:
DRDO works under the administrative control of Ministry of Defence, Government of India.
It is working to establish world class science and technology base for India and provides our Defence Services decisive edge by equipping them with internationally competitive systems and solutions.
DRDO was established in 1958 after combining Technical Development Establishment (TDEs) of the Indian Army and the Directorate of Technical Development & Production (DTDP) with the Defence Science Organisation (DSO).
Dr. Samir V Kamat has taken over as Secretary DDR&D and Chairman Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) on 26th Aug 2022.
Q. 81: Consider the following diseases:
Which of the given above are blood-borne diseases?
Answer: B
Explanation:
Hepatitis B, HIV, and syphilis are blood-borne diseases, meaning they can be transmitted through contact with infected blood.
Hepatitis A is primarily transmitted through ingestion of contaminated food or water, not through blood.
Q. 82: Nullisomy refers to
Answer: A
Explanation:
Nullisomy refers to the condition where an organism loses an entire pair of homologous chromosomes, resulting in a total chromosome count that is two less than the normal diploid number.
Monosomy – the loss of a single chromosome; individuals are called monosomics and their chromosomal composition is 2N- 1.
Q. 83: Which water body separates Australia from New Zealand?
Answer: C
Explanation: The Tasman Sea is the body of water that separates Australia from New Zealand.
Q. 84: The Convention that aims to prevent, detect, and punish match-fixing in sports is known as
Answer: D
Explanation:
Macolin Convention : The Council of Europe Convention on the Manipulation of Sports Competitions better known as the Macolin Convention is a multilateral treaty that aims to prevent, detect, and punish match-fixing in sports. The convention was concluded in Macolin, Switzerland in 2014. A major focus of the convention is to prevent and punish illegal sports betting operations and to prevent conflicts of interest between legal sports betting operators and sports organizations. The 12th meeting of Interpol’s Match-Fixing Task Force (IMFTF) concluded with a call to harmonize global efforts to curb competition manipulation. Central Bureau of Investigation (CBI) was one of the participants at this meeting
Q. 85: Consider the following matches:
Which among the above is / are correct?
Answer: B
Explanation:
Q. 86: Match the following Dams with related
Rivers : Dams Rivers
Choose the correct answer from the options given below :
a b c d
Answer: A
Explanation:
Hirakud Dam is built across the Mahanadi River, about 15 kilometres (9 mi) from Sambalpur in the state of Odisha in India.
The Ranjit Sagar Dam, also known as the Thein Dam, is part of a hydroelectric project constructed by the Punjab Irrigation Department on the Ravi River.
Maharana Pratap Sagar, also known as Pong Reservoir or Pong Dam Lake is a large reservoir in Fatehpur, Jawali and Dehra tehsil of Kangra district of the state of Himachal Pradesh in India. It was created in 1975, by building the highest earthfill dam in India on the Beas River in the wetland zone of the Siwalik Hills.
Salal Dam, also known as Salal Hydroelectric Power Station, is a run-of-the-river hydropower project on the Chenab River in the Reasi district of the Jammu and Kashmir.
Q. 87: The rivers that existed before the upheaval of the Himalayas and cut their courses southward by making gorges in the mountains are known as
Answer: A
Explanation:
A Drainage pattern can be defined in the shadow of topographical features from which a stream gets runoff, through flow, and groundwater flow which can be divided by topographic barriers called a watershed.
Types of drainage patterns found in India
Antecedent or Inconsequent Drainage: Rivers that existed before the upheaval of the Himalayas and cut their courses southward by making gorges in the mountains are known as the antecedent rivers. The Indus, Satluj, Ganga, Sarju (Kali), Arun (a tributary of Kosi), Tista and Brahmaputra are some of the important antecedent rivers, originating from beyond the Greater Himalayas.
Antecedent rivers are those that existed before the uplift of the Himalayas and maintained their course by cutting through the rising mountains, forming deep gorges. Examples of such rivers include the Indus, Sutlej, and Brahmaputra.
Consequent Rivers: The Rivers which follow the general direction of slope are known as the consequent rivers. Most of the rivers of peninsular India are consequent rivers. For example, rivers like Godavari, Krishna and Kaveri, descending from the Western Ghats and flowing into the Bay of Bengal, are some of the consequent rivers of Peninsular India.
Subsequent Rivers: A tributary stream that is eroded along an underlying belt of nonresistant rock after the main drainage pattern (Consequent River) has been established is known as a subsequent river. Due to the northward slope of the Peninsula towards the Great Plains, the rivers originating from the Vindhyan and the Satpura ranges flow northward into the Ganga system. The Chambal, Sind, Ken, Betwa, Tons and Son meet the Yamuna and the Ganga at right angles.
Superimposed, Epigenetic (Discordant) or Superinduced Drainage: It is formed when a stream with a course originally established on a cover of rock now removed by erosion, so that the stream or drainage system is independent of the newly exposed rocks and structures. The Damodar, the Subarnarekha, the Chambal, the Banas and the rivers flowing at the Rewa Plateau present some good examples of superimposed drainage.
Dendritic Drainage: A pattern of drainage which is branching, ramifying or dichotomising, thereby giving the appearance of a tree. Most of the rivers of the Indo-Gangetic Plains are of dendritic type.
Trellis Drainage: It is a rectangular pattern formed where two sets of structural controls occurs at right angles. In a trellis pattern, the river forms a net like system and the tributaries flow roughly parallel to each other. The old folded mountains of the Singhbhum (Chotanagpur Plateau) have drainage of trellis pattern.
Barbed Pattern: A pattern of drainage in which the confluence of a tributary with the main river is characterised by a discordant junction—as if the tributary intends to flow upstream and not downstream. This pattern is the result of capture of the main river which completely reverses its direction of flow, while the tributaries continue to point in the direction of former flow. The Arun River (Nepal), a tributary of the Kosi is an interesting example of barbed drainage pattern.
Rectangular Drainage: The drainage pattern marked by right-angled bends and right-angled junctions between tributaries and the main stream is known as rectangular drainage. It differs from the trellis pattern in so far as it is more irregular and its tributary streams are neither as long, nor parallel as in trellis drainage. A typical example of this drainage pattern is found is the Vindhyan Mountains of India.
Radial Pattern: It is a pattern characterised by out flowing rivers, away from a central point, analogous with the spokes of a wheel. It tends to develop on the flanks of a dome or a volcanic cone. A good example of a radial drainage pattern is provided by the rivers originating from the Amarkantak Mountain. Rivers like Narmada, Son and Mahanadi originating from Amarkantak Hills flow in different directions and are good examples of radial pattern. This pattern is also found in the Girnar Hills (Kathiwar, Gujarat), and Mikir Hills of Assam.
Annular Pattern: In this drainage pattern, the subsequent streams follow curving or actuate courses prior to joining the consequent stream. This results from a partial adaptation to an underground circular struc-ture; a dome like igneous intrusion (batholith). The subsequent streams find it easier to erode the concentric, less resistant strata. This is not a very common drainage pattern in India. Some examples of this are however found in Pithoragarh (Uttarakhand), Nilgiri Hills in Tamil Nadu and Kerala.
Parallel Drainage: The drainage pattern in which the rivers flow almost parallel to each other is known as parallel drainage. The small and swift rivers originating in the Western Ghats and discharging their water into the Arabian Sea provide a good example of parallel drainage pattern in India.
Deranged Pattern: This is an uncoordinated pattern of drainage characteristic of a region recently vacated by an ice-sheet. This is probably due to the irregularities produced by glacially deposited materials, e.g., Kame and Kettle, and by the fact that there has been insufficient time for the drainage to become adjusted to the structures of the solid rock underlying the glacial drift. The picture is one of numerous water courses, lakes and marshes; some inter-connected and some in local drainage basins of their own. This type of drainage is found in the glaciated valleys of Karakoram.
Q. 88: Which one of the following is not a Biosphere reserve?
Answer: B
Explanation:
Nallamalai is not a biosphere reserve. It is hill of Eastern ghats which stretches over districts of Andra Pradesh and Telengana.
Biosphere reserves are areas of terrestrial and coastal ecosystems promoting solutions to reconcile the conservation of biodiversity with its sustainable use. They are internationally recognized, nominated by national governments and remain under sovereign jurisdiction of the states where they are located.
Biosphere Reserves in India : There are 18 biosphere reserves in India:
Q. 89: Who among the following is the author of the famous book “Silent Spring”?
Answer: A
Explanation: Rachel Carson authored the famous book “Silent Spring,” which was published in 1962. The book is credited with advancing the global environmental movement by highlighting the adverse effects of pesticides on the environment.
Q. 90: ‘Global Innovation and Technology Alliance (GITA)’, a platform encouraging industrial investments in innovative technology is jointly developed by Department of Science & Technology (DST) and
Answer: C
Explanation: The Global Innovation and Technology Alliance (GITA) is a joint venture between the Technology Development Board (TDB) of the Department of Science & Technology (DST) and the Confederation of Indian Industry (CII). It aims to stimulate private sector investment in research and development by fostering collaborations between industry, academia, and government
Q. 91: The report “Assessment of Climate Change over the Indian Region” has been released by which of the following?
Answer: D
Explanation: The Ministry of Earth Sciences (MoES) published the report titled “Assessment of Climate Change over the Indian Region,” which provides a comprehensive assessment of the impact of climate change on the Indian subcontinent.
Q. 92: Project UNNATI has been started by the Government of India to:
Answer: D
Explanation: Project UNNATI is an initiative by the Government of India aimed at identifying and improving the operational efficiency of major ports in the country. It focuses on enhancing port infrastructure, optimizing operations, and boosting overall productivity.
Q. 93: ‘Neom city’ often seen in the news, is a futuristic megacity that will be constructed in which of the following countries?
Answer: C
Explanation: Neom City is a futuristic megacity being constructed in Saudi Arabia.
Q. 94: In which of the following groups are all the four countries members of the Shanghai Cooperation Organisation?
Answer: B
Explanation:
Shanghai Cooperation Organisation: The Shanghai Cooperation Organisation (SCO) is a prominent intergovernmental organization founded on June 15, 2001, in Shanghai, China. Initially established by six countries—China, Russia, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, and Uzbekistan—the SCO has since expanded to include ten full member states as of 2024.
The primary goals of the SCO are:
The SCO’s governance structure includes several key bodies:
Heads of State Council (HSC): The supreme decision-making body that meets annually to address significant issues.
Heads of Government Council (HGC): Focuses on economic cooperation and approves the organization’s budget.
Regional Anti-Terrorist Structure (RATS): Coordinates counter-terrorism efforts among member states.
Q. 95: Which of the following statements is the most appropriate explanation of ‘FASTags’?
Explanation: FASTags are Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) tags that enable automatic deduction of toll charges at toll plazas. They are affixed on the windscreen of vehicles and allow for cashless transactions, reducing wait times and congestion at toll booths.
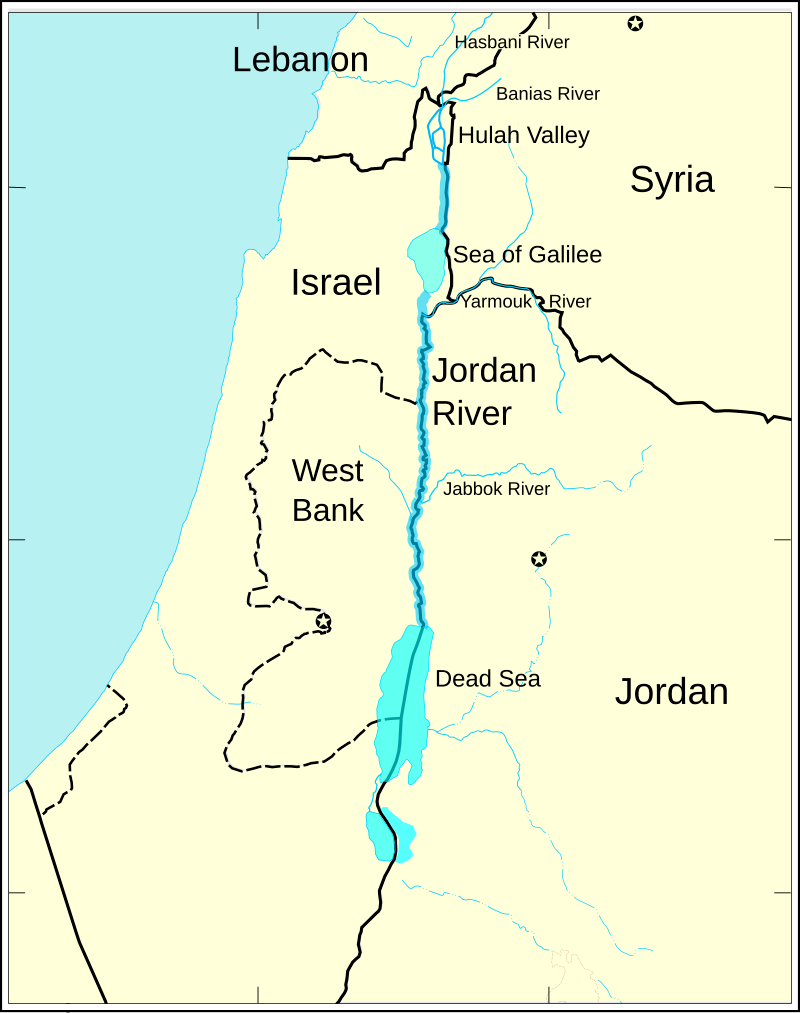
Q. 96: West Bank’ is not bordered by
Answer: A
Explanation:
The West Bank is bordered by Israel, Jordan, and the Dead Sea, but not Syria.
Q. 97: Consider the following statements:
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
Answer: A
Explanation:
An application programming interface (API) is a set of rules and protocols that allows software applications to communicate with each other. APIs act as an intermediary, allowing different software components to interact and perform tasks.
APIs are important because they:
APIs allow third-party applications and trading systems to access data from stock and futures markets.
Q. 98: Consider the following statements:
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
Answer: D
Explanation:
Li-Fi is a light communication system that is capable of transmitting data at high speeds over the visible light, ultraviolet, and infrared spectrums.
WiFi transmits data using radio waves, whereas Li-Fi uses light, typically from LED bulbs, to transmit data. Li-Fi operates at a frequency spectrum about 10,000 times higher than WiFi, offering potentially higher data transmission speeds.
LiFi (light fidelity) is a bidirectional wireless system that transmits data via LED or infrared light.
Li-Fi is a wireless communication technology that uses light to transmit data, while NFC (Near Field Communication) is a contactless payment technology that uses wireless technology to transmit payment information:
Li-Fi: Li-Fi is a wireless communication technology that uses light to transmit data. It uses LED lights to emit light pulses that contain information, which is then decoded by devices with the appropriate receivers. Li-Fi can transmit data at high speeds over visible, ultraviolet, and infrared spectrums. It can be used in areas that are susceptible to electromagnetic interference, such as aircraft cabins, hospitals, or the military.
NFC: NFC is a contactless payment technology that uses wireless technology to transmit payment information to a payment terminal. For example, Google Pay’s “Tap to pay for UPI” feature uses NFC technology to allow users to make transactions by tapping their phones on a point-of-sale terminal.
Q. 99: Consider the following statements:
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
Answer: C
Explanation:
Quantum computing is a field of computer science that uses quantum mechanics to perform calculations faster than classical computers. Quantum computers use the unique properties of quantum physics, such as superposition, entanglement, and quantum interference, to solve complex problems.
Quantum computing has the potential to revolutionize the ability to solve problems that are currently impossible for even the most powerful supercomputers. Some applications where quantum computers can provide a speed boost include: machine learning, optimization, simulation of physical systems, portfolio optimization in finance, and simulation of chemical systems.
Quantum computing is a multidisciplinary field that includes hardware research and application development. It’s still in development, but quantum technology will soon be able to solve complex problems that supercomputers can’t solve, or can’t solve fast enough.
The Department of Energy (DOE) and NASA are both supporting quantum computing research. NASA’s Quantum Artificial Intelligence Laboratory (QuAIL) is a hub for assessing and advancing the potential of quantum computers.
Cloud computing is the delivery of computing resources, like storage, servers, and databases, over the internet on demand. It allows users to pay for services as they use them, instead of buying and maintaining physical resources.
Cloud computing offers several benefits, including:
Some examples of cloud computing services include:
Q. 100: Which one of the following pair is incorrect with regards to Nobel Prize in 2024?
Answer: D
Explanation:
Nobel Prize in 2024
Nobel Prize in Physics 2024
Nobel Prize in Chemistry 2024
Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 2024
Nobel Prize in Literature 2024
Nobel Peace Prize 2024
Nobel Prize in Economic Sciences 2024